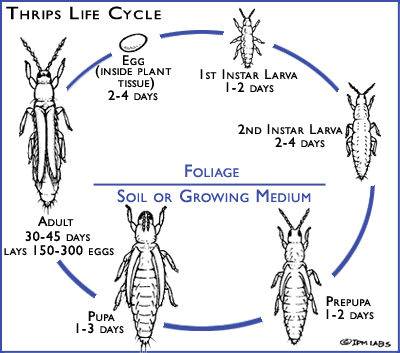
Thrips life cycle
Thrips Control on Plants starts with understanding the thrips life cycle. Including thrips’ activity habits, breeding methods, preferred environmental conditions, and peak occurrence periods.
- Activity habits: Thrips like warm, dry weather. Likes to be active at 23℃ to 28℃. The suitable air humidity is 40% to 70%. They are usually hidden during the day in backlit areas such as the undersides of leaves, in the soil, or inside flowers. It is only active on the surface of the host at night and on cloudy days. Thrips adults and nymphs use their mouthparts to suck the sap from young plant tissues.
- Reproduction method: Female adults of thrips mainly reproduce parthenogenetically. Occasionally, hermaphroditic reproduction occurs, but males are extremely rare.
- Peak period of occurrence: The peak period of thrips occurrence varies from region to region. It is generally more common in spring and autumn.
- Characteristics: Thrips have the characteristics of tending to be tender, liking sweetness, tending to be blue, and being afraid of light and moisture. They reproduce quickly. Short life cycle. Therefore, under suitable conditions, they can multiply quickly and cause disasters.
Additionally, thrips thrive especially in poorly managed soil environments. For example, soil compaction in the rainy season or long-term rainy weather will adversely affect its survival.
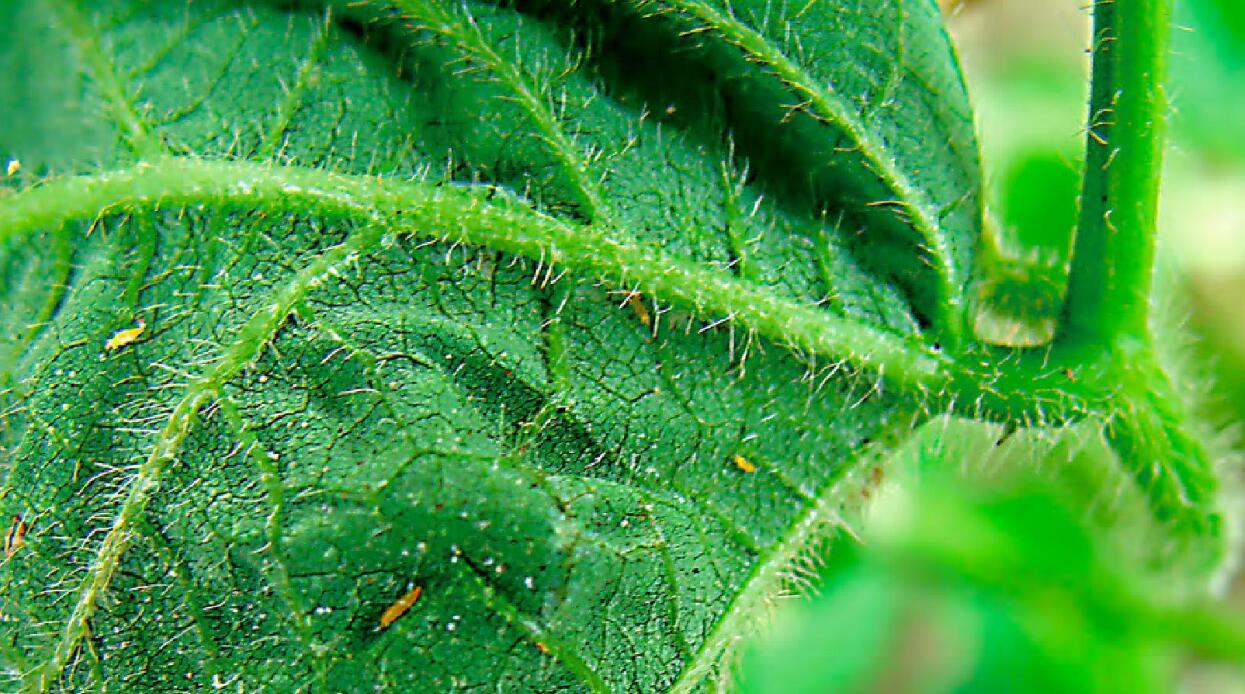
Thrips damage
- Damage to leaves and young shoots
The tender tips of the young leaves become hard, curled and withered. There are dense white spots or long strips on the leaf surface. In the later stage, the leaf veins turn dark brown, the internodes of the injured tender tips become shorter and the growth is slow.
Long strips or spots of yellow-white or silver-gray patches appear on the back of the leaves. In the later stages, the patches become chlorotic, yellow and withered, and the leaf veins turn dark brown. The leaves gradually shrink and dry up.
- Damage to flower organs and tender fruits
The flower organs are damaged and appear as white spots at first, then turn brown and gradually wither.
If the fruit is damaged, scars will occur. The scars expand as the fruit enlarges. Showing different shapes and varying degrees of corkization. In severe cases, fruit drop may occur.
3.Others
In addition to directly damaging plants, thrips can also spread viral diseases. For example, cholera, dysentery, etc.

Thrips Control on Plants
Thrips control methods mainly include agricultural control, physical control, chemical control and biological control.
- Agricultural prevention and control:
By cleaning the fields, weeds and dead leaves in the fields are eradicated in a timely manner. And burn them together or bury them deeply. Eliminate insect sources and reduce thrips habitat.
Strengthen fertilizer and water management and cultivate robust plants to enhance crop growth and reduce losses caused by thrips.
Water at the right time to prevent drought and create a small field environment that is not conducive to the survival of thrips. - Physical prevention:
Taking advantage of thrips’ tendency towards blue, blue boards are hung in the field to trap and kill adult insects. The height of the sticky board should be flush with the crops. - Chemical control. Use thiamethoxam, imidacloprid, spinosad and other chemicals for control. These pesticides can be used through spraying, seed dressing, soil treatment, root irrigation, etc. Pay attention to the selection and timing of pesticide use, and adjust the medication strategy according to the resistance of thrips.
- Biological control: Biological pesticides such as emamectin, matrine, etc. can be used to control thrips.
In addition, please note that thrips are highly concealed. Choosing agents with strong systemic properties or adding silicone additives can improve the control effect. Prevention is key. Don’t wait until thrips are overrun before you start controlling them
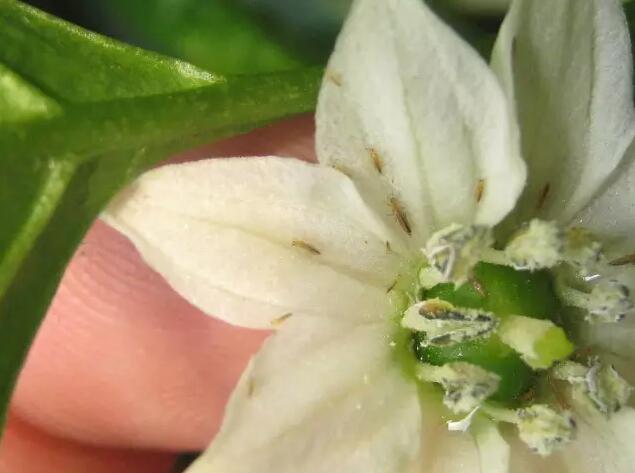

When growing vegetables during periods of high temperatures and humidity. If there is no mulch, it is best to spray the middle and lower parts of the plant and the ground at the same time. Because these places are home to thrips nymphs.






